Welcome to the fascinating world of red clover, a petite flowering plant with big promises for health. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll unravel the mysteries surrounding red clover, examining its uses, potential side effects, precautions, interactions, dosing, and user reviews. Let’s embark on a journey to understand the benefits and considerations associated with this herbal remedy.
Table of Contents
- Overview of Red Clover
- Uses and Effectiveness: A Blank Canvas
- How to Use Red Clover Safely?
- Dosing Guidelines: Navigating the Spectrum
- User Guide: Navigating Information
- Conclusion
Overview of Red Clover
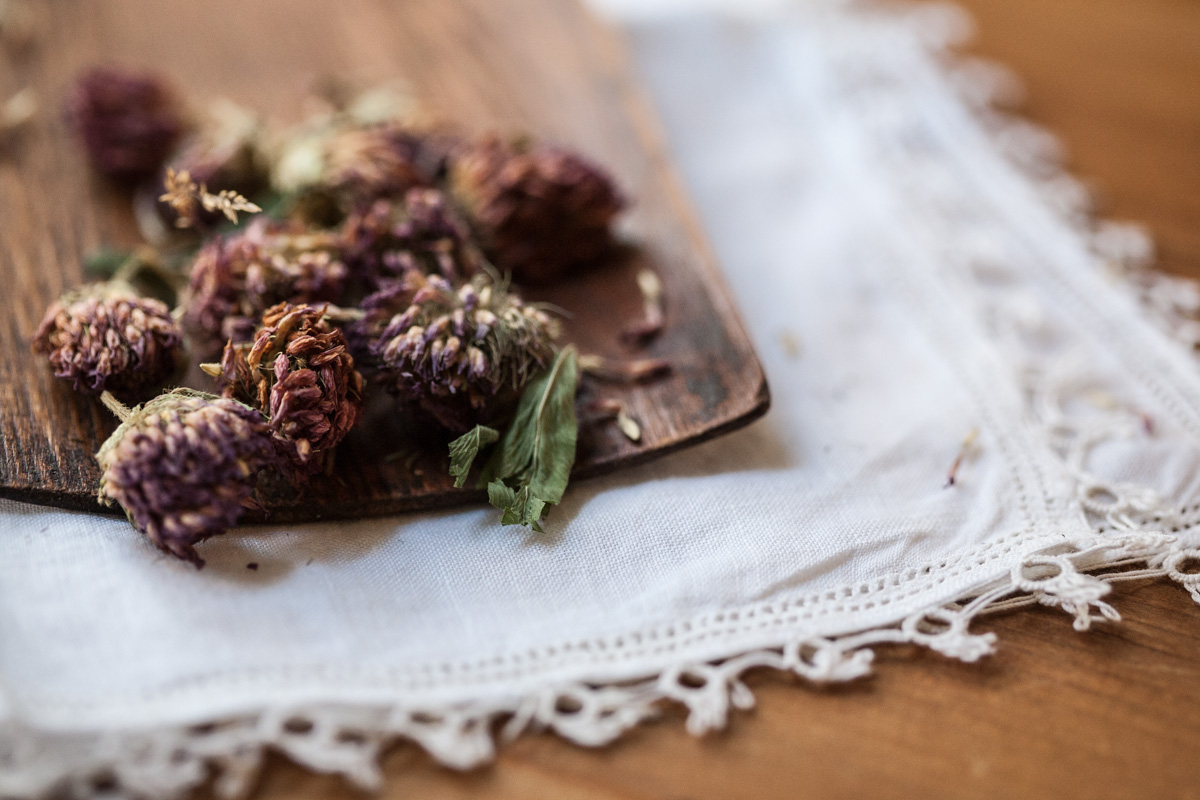

Red clover, scientifically known as Trifolium pratense, is not just a charming addition to your garden. This legume, standing at 15-40 cm tall, is making waves in the health and wellness community. Found in regions including Europe, central Asia, and northern Africa, red clover contains phytoestrogens, compounds akin to the hormone estrogen.
Traditionally eaten as a legume and used in supplements marketed for female health, red clover’s popularity stems from its potential to address various health concerns. However, it’s essential to note that while people commonly use red clover for symptoms like menopause, weak bones, breast pain, and more, scientific evidence supporting these uses is currently lacking.
Uses and Effectiveness: A Blank Canvas
When it comes to the uses of red clover, the canvas is surprisingly blank. Despite being a common ingredient in female health supplements, concrete scientific information on its applications is elusive. As research progresses, we may uncover more about the potential benefits of this unassuming plant.
If you are looking for a natural way to improve your health and well-being, you might have heard of red clover. This plant has been used for centuries as a food and medicine, and it has many benefits for the body and mind. But before you start using red clover, you should be aware of some important facts. Here are some tips on how to use red clover safely and effectively.
How to Use Red Clover Safely?
Red clover can be consumed in different ways, such as in foods, teas, capsules, or creams. However, not all forms of red clover are equally safe or effective. Here are some guidelines on how to use red clover safely:
- By mouth: Eating red clover in foods or taking supplements is generally safe for most people. You can take up to 80 mg of isoflavones per day for up to two years without any serious side effects. However, some people may experience minor side effects, such as muscle pain, nausea, or vaginal bleeding. If you have any of these symptoms, stop using red clover and consult your doctor.
- On the skin: Applying red clover on the skin is safe for short-term use, up to four weeks. This can help with skin conditions, such as eczema, psoriasis, or acne. You can use creams or lotions that contain red clover extract or make your own by infusing red clover flowers in oil.
- Special precautions and warnings: While red clover is safe for most people, there are some situations where you should avoid using it. These include:
- Pregnancy and breast-feeding: Using red clover medicinally during pregnancy or breast-feeding is potentially unsafe. Red clover’s estrogen-like effects could interfere with your hormonal balance and affect your baby’s development. Therefore, it is best to avoid using red clover during these periods.
- Hormone-sensitive conditions: If you have a condition that is sensitive to estrogen, such as breast cancer or uterine fibroids, you should be careful with red clover. Red clover’s estrogenic properties may worsen your condition and increase your risk of complications. Therefore, it is best to avoid using red clover if you have a hormone-sensitive condition or consult your doctor before using it.
- Interactions: Red clover can interact with some medications and affect their effectiveness or safety. Here are some examples of medications that can interact with red clover:
- Estrogen: Taking red clover with estrogen may reduce the effects of estrogen. This could make your hormone therapy less effective or cause unwanted side effects. Therefore, it is best to avoid taking red clover with estrogen or consult your doctor before doing so.
- Tamoxifen: Tamoxifen is a medication that blocks the effects of estrogen in the body. It is used to treat or prevent breast cancer. Taking red clover with tamoxifen may decrease the effectiveness of tamoxifen and increase your risk of breast cancer recurrence. Therefore, it is best to avoid taking red clover with tamoxifen or consult your doctor before doing so.
- Methotrexate: Methotrexate is a medication that lowers the activity of the immune system. It is used to treat various conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis or psoriasis. Taking red clover with methotrexate may increase the levels of methotrexate in your body and cause more side effects. Therefore, it is best to avoid taking red clover with methotrexate or consult your doctor before doing so.
- Blood thinners: Blood thinners are medications that prevent blood clots from forming in your blood vessels. They are used to treat or prevent conditions such as stroke or heart attack. Taking red clover with blood thinners may increase your risk of bleeding or bruising. Therefore, it is best to avoid taking red clover with blood thinners or consult your doctor before doing so.
- Liver medications: Liver medications are medications that affect how your liver breaks down other substances in your body. They include drugs such as acetaminophen or statins. Taking red clover with liver medications may alter the effects of these drugs and cause more side effects. Therefore, it is best to avoid taking red clover with liver medications or consult your doctor before doing so.
Dosing Guidelines: Navigating the Spectrum
For adults, the typical doses of red clover range from 40-80 mg by mouth daily for up to one year. However, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare provider to determine the best product and dose tailored to specific conditions.
User Guide: Navigating Information
This information is a supplement to professional advice, sourced from the Natural Medicines Comprehensive Database Consumer Version. Always consult healthcare providers for personalized guidance, ensuring a tailored approach to individual health.
Conclusion
Red clover is a natural plant that has many benefits for your health and well-being. However, it also has some potential risks and interactions that you should be aware of. To use red clover safely and effectively, follow these tips:
- Choose the right form of red clover for your needs and preferences.
- Use red clover in moderation and follow the recommended dosage and duration.
- Avoid using red clover if you are pregnant, breast-feeding, or have a hormone-sensitive condition.
- Check with your doctor before using red clover if you are taking any medications that can interact with it.
By following these tips, you can enjoy the benefits of red clover without compromising your safety or health.