Indulging in oily food cravings occasionally is a common temptation for many, but mitigating the aftereffects is crucial for maintaining overall health and well-being. Oily foods, laden with trans fats and saturated fats, pose various health risks, including obesity, elevated cholesterol levels, and heart disease. However, adopting certain post-consumption strategies can help counteract these effects and promote digestive health and vitality. Let’s explore practical steps to take after eating oily food to restore balance and support your body’s natural functions.
Replenish with Lukewarm Water
Hydrating your body with lukewarm water after consuming oily food is essential for aiding digestion and soothing your digestive system. Lukewarm water facilitates the breakdown of nutrients, promoting their absorption and utilization by the body. Unlike ice-cold water, which can impair digestion by diluting stomach acid, lukewarm water supports optimal digestive function without imposing additional stress on your system.
Harness the Power of Detox Drinks
Detox drinks offer a natural means of flushing out toxins accumulated from oily food consumption, promoting detoxification and metabolic balance. Lemon water, renowned for its cleansing properties, aids in fat metabolism and may facilitate weight loss. While scientific evidence supporting the efficacy of detox programs is inconclusive, incorporating detox drinks into your routine can serve as a refreshing and revitalizing post-meal ritual.
Embrace Physical Activity
Engaging in light physical activity, such as walking, for 30 minutes after a heavy meal can significantly enhance digestion and promote overall well-being. Walking stimulates gastrointestinal motility, facilitating the movement of food through the digestive tract and alleviating symptoms of bloating and discomfort. Additionally, regular physical activity supports weight management and metabolic health, contributing to long-term vitality.
Strategize Your Meal Planning
Planning your meals mindfully can help prevent impulsive consumption of oily and unhealthy foods. Prioritize nutrient-dense, whole foods in your diet, incorporating ample fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins to support optimal health and vitality. Opt for smaller, more frequent meals to prevent overeating and promote steady energy levels throughout the day. By proactively planning your meals, you can cultivate healthier eating habits and minimize the temptation of indulging in oily foods.
Nourish Your Gut with Probiotics
Integrating probiotic-rich foods into your diet, such as yogurt or fermented soy products, promotes gut health and enhances digestive function. Probiotics help maintain a healthy balance of gut bacteria, supporting immune function and nutrient absorption. Incorporating probiotics into your post-oily food regimen can aid in restoring digestive harmony and mitigating gastrointestinal distress.
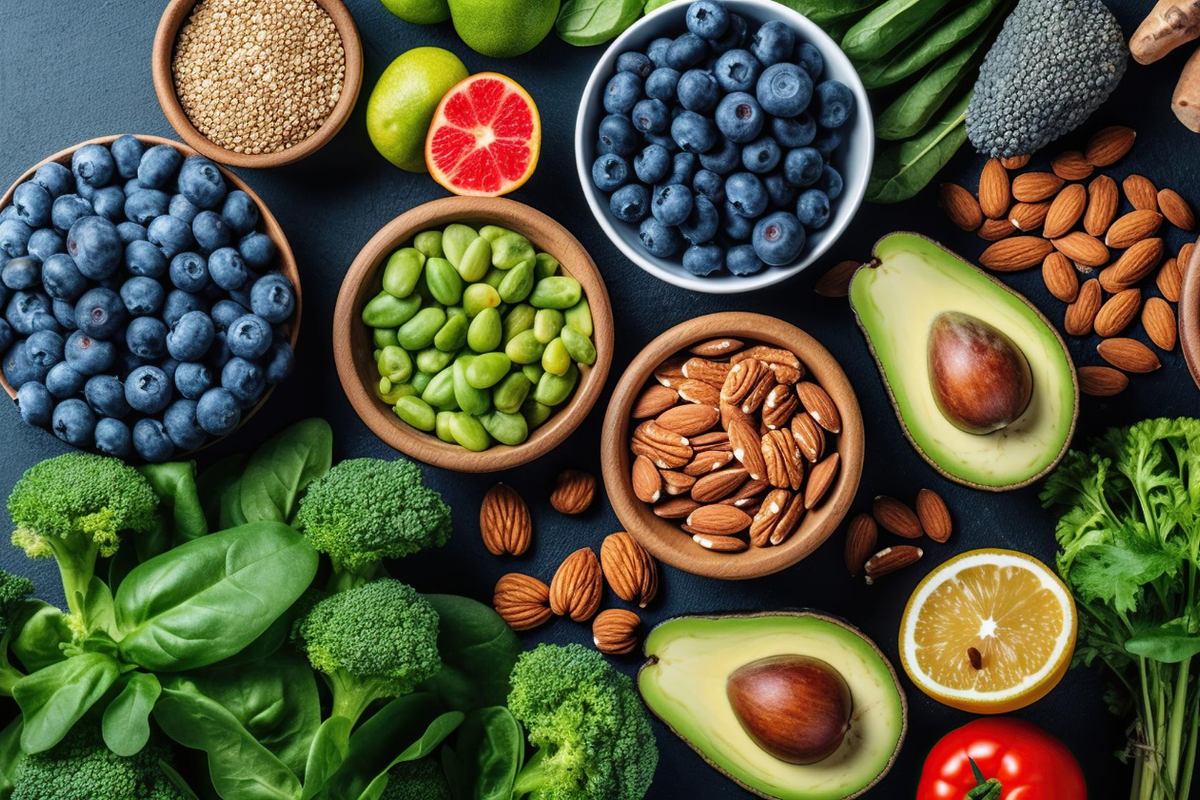
Prioritize Fiber-Rich Foods
Consuming fiber-rich foods after oily food consumption is essential for promoting digestive regularity and supporting overall health. Fruits and vegetables provide essential vitamins, minerals, and dietary fiber, which aid in digestion and promote satiety. Incorporating fiber-rich snacks, such as mixed fruit bowls or leafy green salads, into your routine can help offset the nutritional imbalances associated with oily food consumption and promote gastrointestinal health.
Promote Restful Sleep
Prioritizing restful sleep is essential for supporting overall health and well-being, particularly after indulging in oily foods. Quality sleep promotes metabolic balance, enhances mood, and facilitates optimal digestive function. Avoiding heavy meals and excessive alcohol consumption before bedtime can help optimize sleep quality and minimize post-meal discomfort. By prioritizing restorative sleep, you can support your body’s natural healing processes and maintain vitality.
Incorporate Digestive Aids
Digestive bitters and enzyme supplements offer additional support for optimal digestion, particularly after consuming oily foods. Bitters stimulate digestive secretions and promote nutrient absorption, while digestive enzymes facilitate the breakdown of fats, proteins, and carbohydrates. Integrating these digestive aids into your post-meal routine can alleviate digestive discomfort and promote overall well-being.
Conclusion
In conclusion, adopting proactive strategies after consuming oily food is essential for mitigating the associated health risks and promoting digestive health and vitality. By prioritizing hydration, physical activity, and nutrient-dense foods, you can support your body’s natural detoxification processes and restore balance. Incorporating probiotics, fiber-rich foods, and digestive aids into your routine can further enhance digestive function and promote overall well-being. Remember to prioritize restful sleep and mindful meal planning to optimize your body’s response to oily food consumption and maintain long-term health and vitality.