Are you looking for the perfect pre-workout snack to boost your energy levels and enhance your performance at the gym or on the track? We’ve got you covered! In this article, we’ll explore a variety of pre-workout snack ideas that will help you power through your workouts and achieve your fitness goals. Whether you’re an early bird hitting the gym or an evening enthusiast heading out for a run, the right fuel can make all the difference.
The Importance of Pre-Workout Nutrition
Before we dive into the delicious snacks, let’s understand why pre-workout nutrition is so vital. When you exercise, your body requires fuel to perform at its best. Proper nutrition before a workout can help in several ways:
- Boost Energy: Pre-workout snacks provide you with a quick energy boost, so you can give your all during your exercise routine. Eating carbs before exercise can increase your glycogen stores, which are your muscles’ main source of energy for short and high intensity workouts.
- Enhance Endurance: The right food can help you exercise for a more extended period, allowing you to push your limits. Eating protein before exercise can enhance muscle protein synthesis, which is the process of building and repairing muscle tissue. Protein can also prevent muscle breakdown and reduce fatigue.
- Improve Focus: Pre-workout nutrition can enhance mental focus and concentration, helping you stay on track with your workouts. Caffeine is a common ingredient in many pre-workout supplements, and it can improve alertness, mood, and cognitive function . Caffeine can also reduce perceived exertion, making your workout feel easier .
- Aid Muscle Recovery: Certain snacks can aid in muscle recovery, reducing post-workout soreness. Creatine is another popular supplement that can increase muscle mass, strength, and power . Creatine can also speed up muscle recovery by increasing the rate of glycogen replenishment .
Now, let’s explore some delicious pre-workout snack options:
1. Banana and Almond Butter
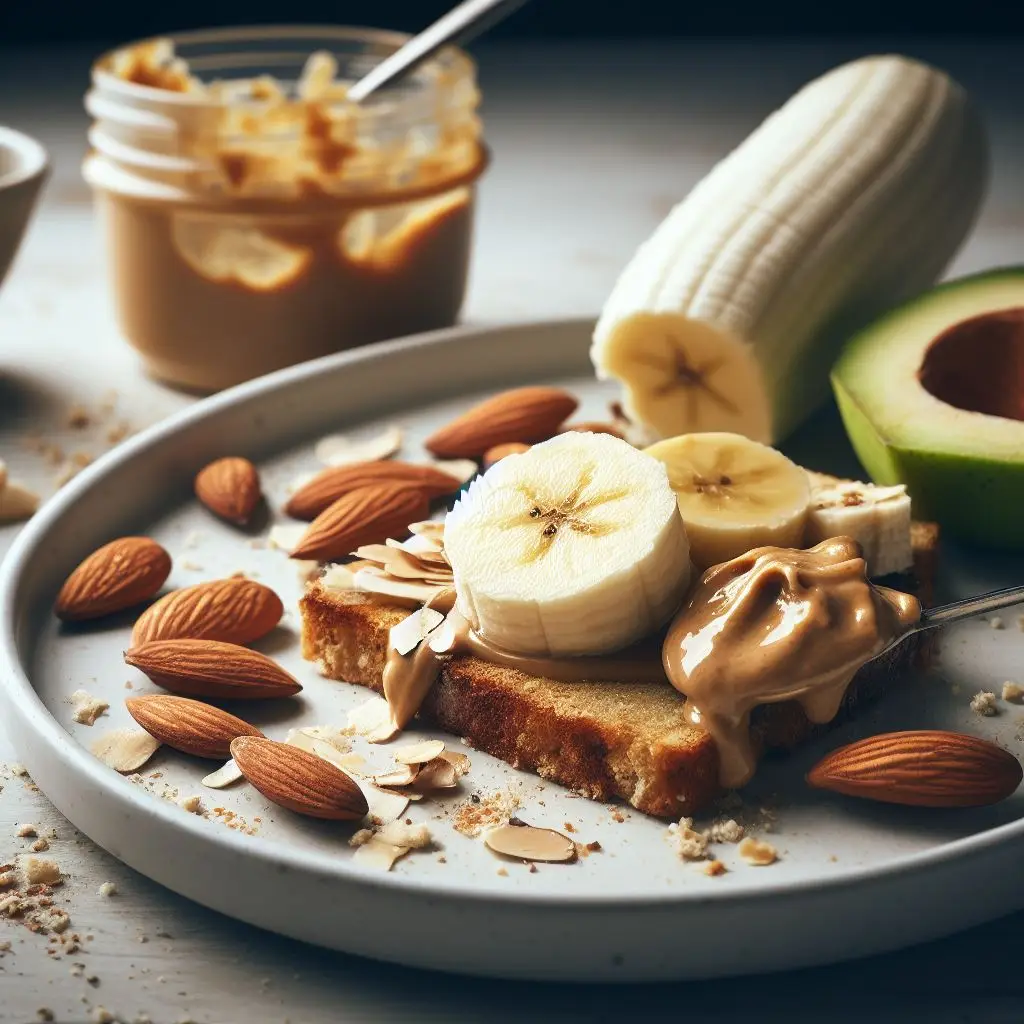

One of the simplest and most effective pre-workout snacks is a banana with a generous spread of almond butter. The banana provides a quick source of natural sugars, while almond butter offers healthy fats and protein. It’s a winning combination to fuel your workout.
2. Greek Yogurt Parfait
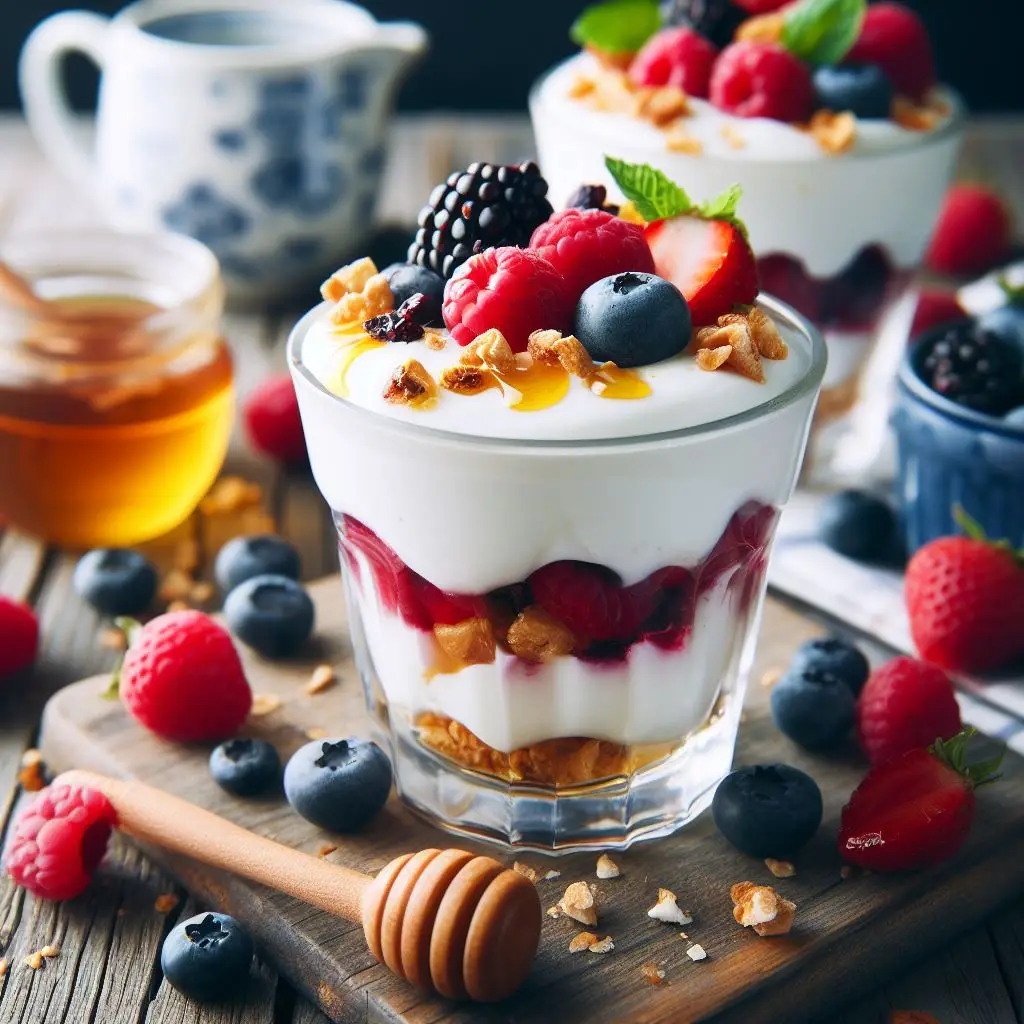

Combine Greek yogurt with fresh berries and a drizzle of honey. This snack is rich in protein, probiotics, and antioxidants, making it an ideal choice for boosting your workout performance.
3. Oatmeal with Berries
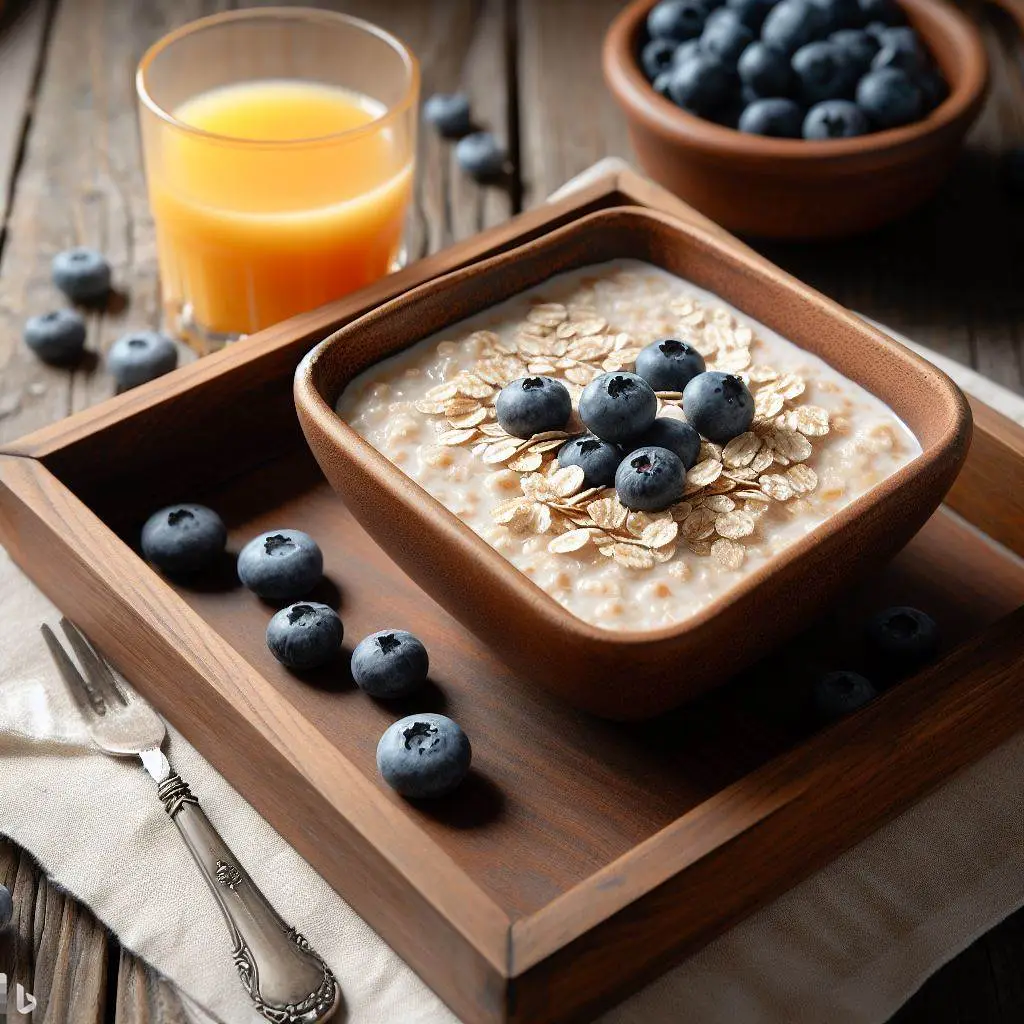

Oatmeal is an excellent source of complex carbohydrates. Top it with a handful of fresh berries for a nutritious and energy-boosting pre-workout snack.
4. Rice Cakes with Avocado
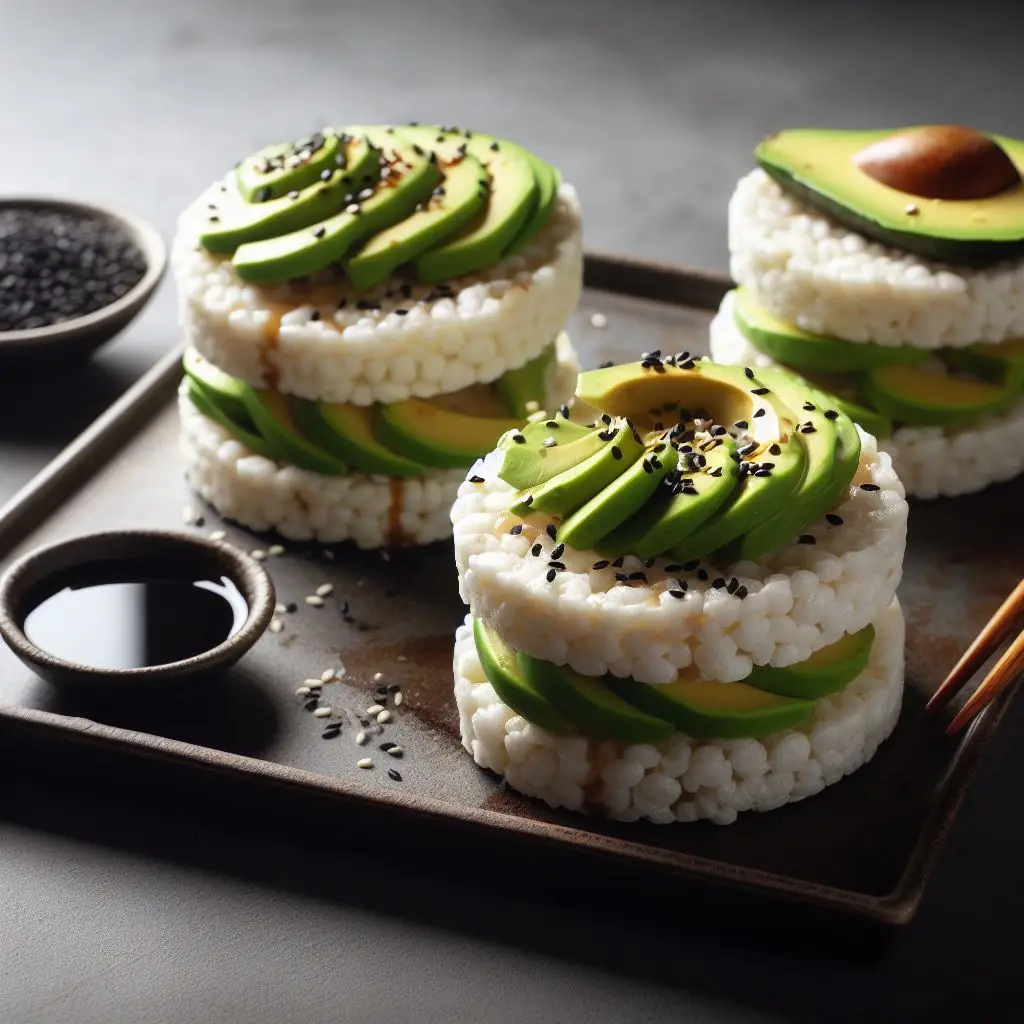

Spread mashed avocado on rice cakes for a healthy dose of monounsaturated fats and fiber. It’s a great choice for those looking for a light yet satisfying snack.
5. Protein Smoothie
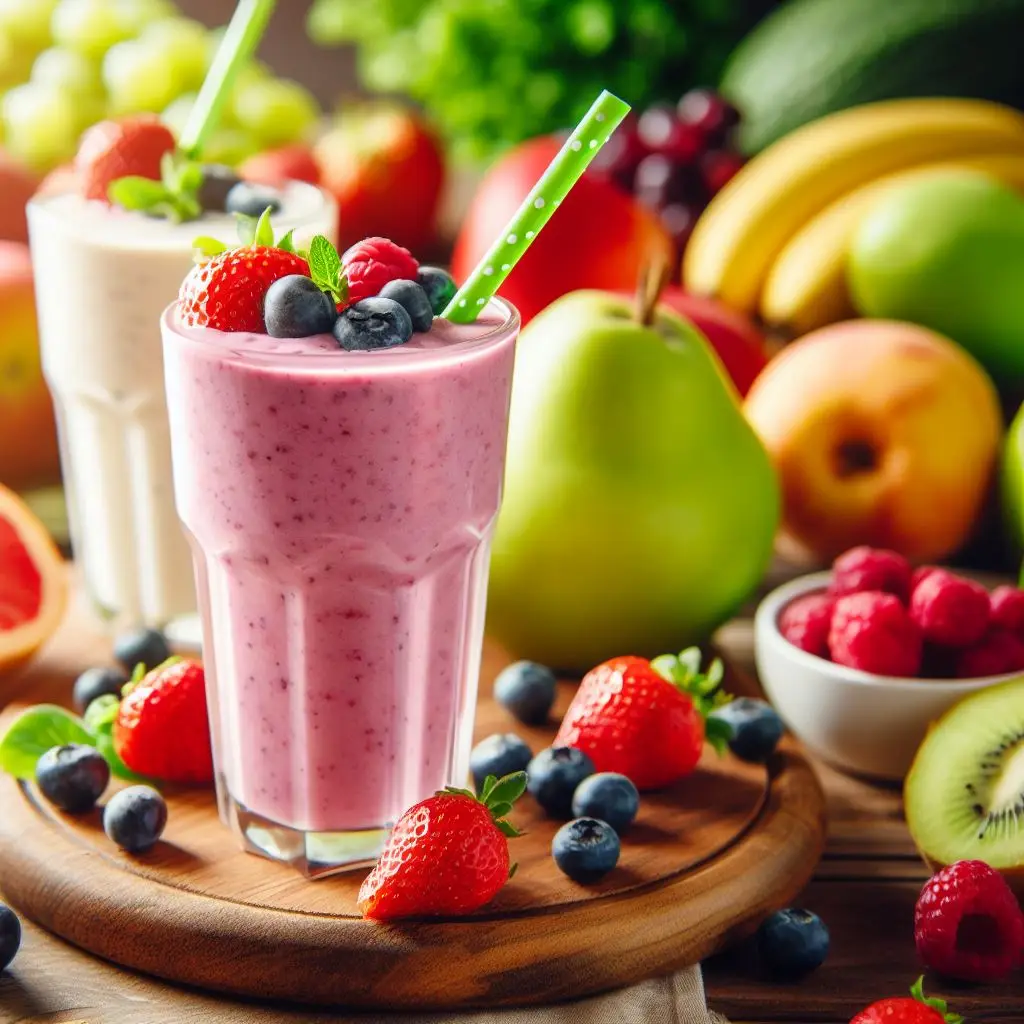

Whip up a protein smoothie with your favorite protein powder, almond milk, a banana, and some spinach. This powerful blend provides a protein-packed punch to get you through your workout.
6. Whole Grain Toast with Cottage Cheese
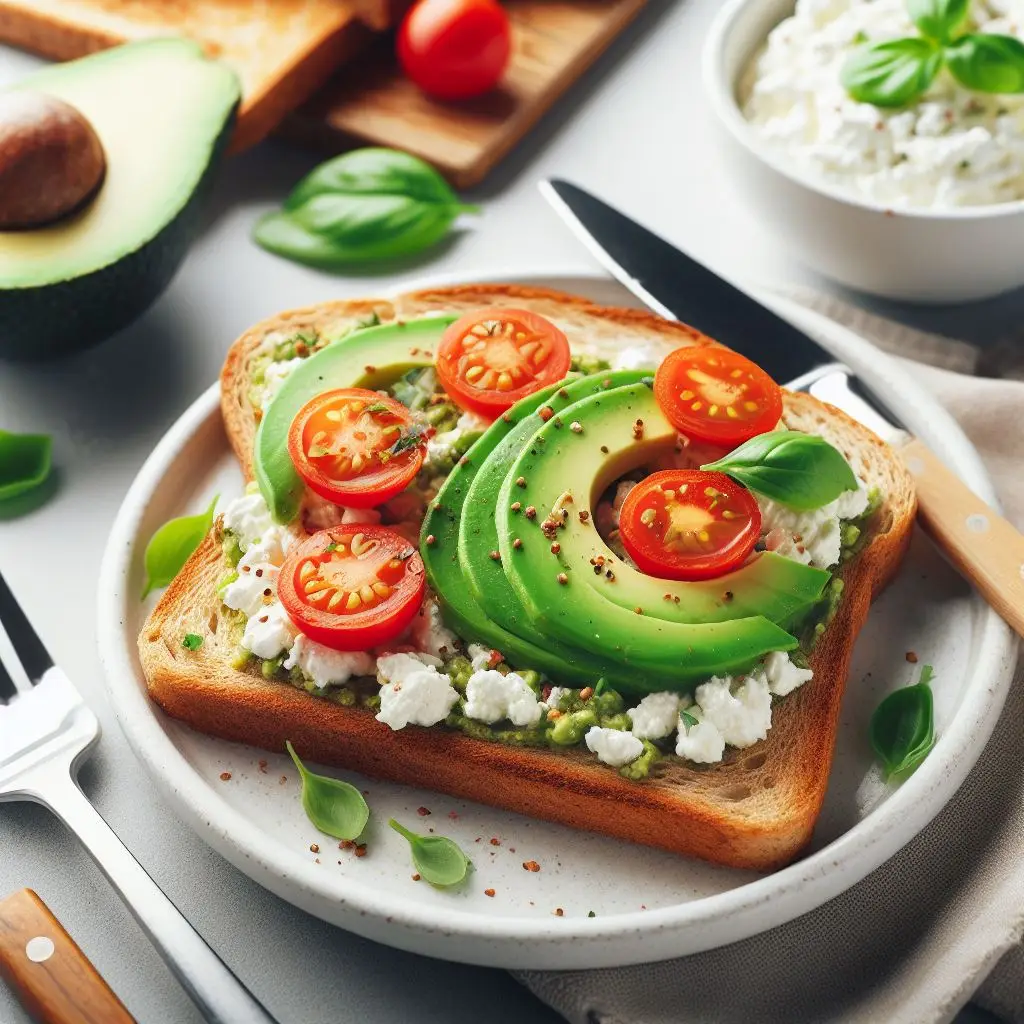

Whole grain toast topped with a generous serving of cottage cheese is an excellent source of protein and complex carbohydrates. It’s a simple and tasty snack option.
7. Trail Mix
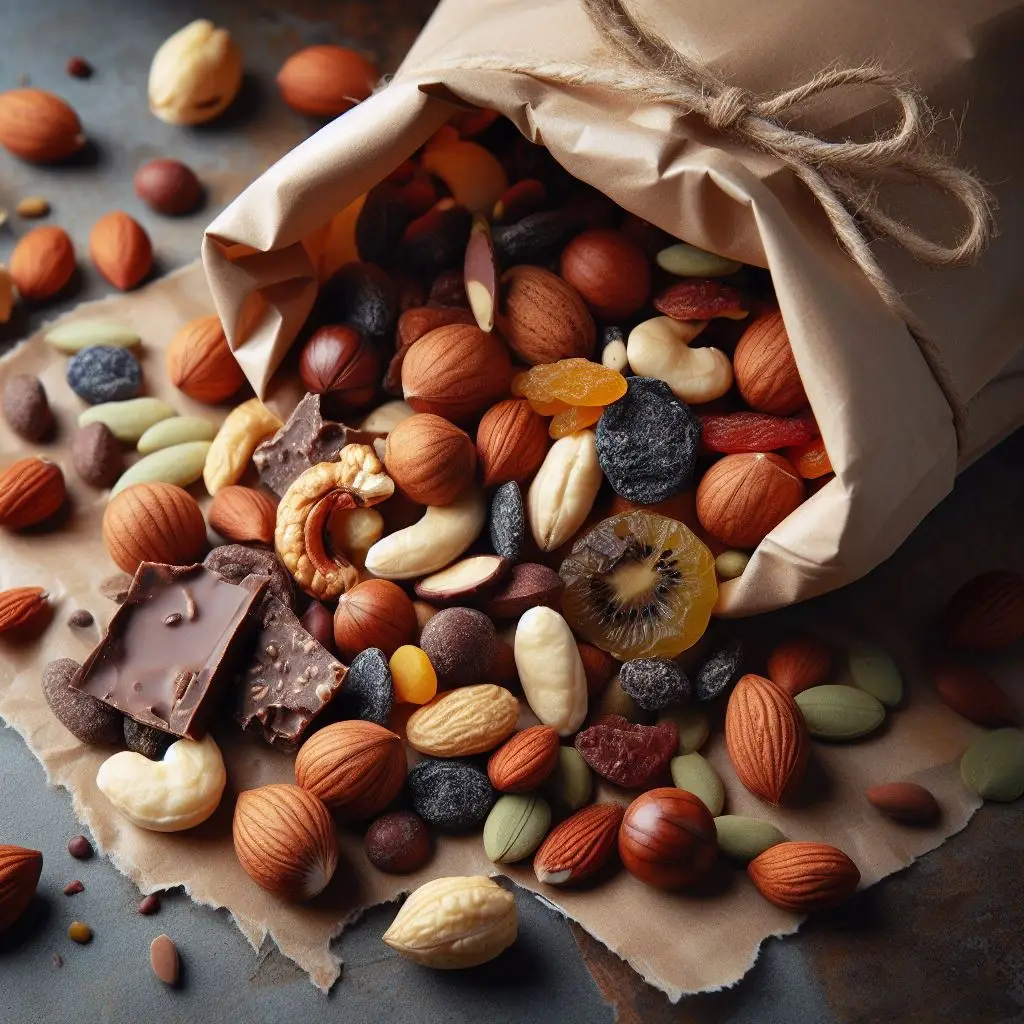

Create your custom trail mix with a variety of nuts, dried fruits, and a touch of dark chocolate. It’s a convenient and energy-dense snack for on-the-go athletes.
8. Hummus and Veggies

Dip colorful vegetable sticks in creamy hummus for a snack that’s packed with fiber, vitamins, and minerals. It’s a refreshing choice before your workout.
9. Hard-Boiled Eggs

Hard-boiled eggs are an excellent source of protein and healthy fats. They’re portable, making them a convenient pre-workout snack for those with a busy schedule.
10. Peanut Butter and Banana Sandwich

Create a classic sandwich with whole-grain bread, peanut butter, and banana slices. It’s a tasty and energy-rich option for a quick pre-workout bite.
11. Apple Slices with Nut Butter

Slice an apple and pair it with your favorite nut butter. This combination offers a satisfying mix of carbohydrates, fiber, and healthy fats.
12. Quinoa Salad
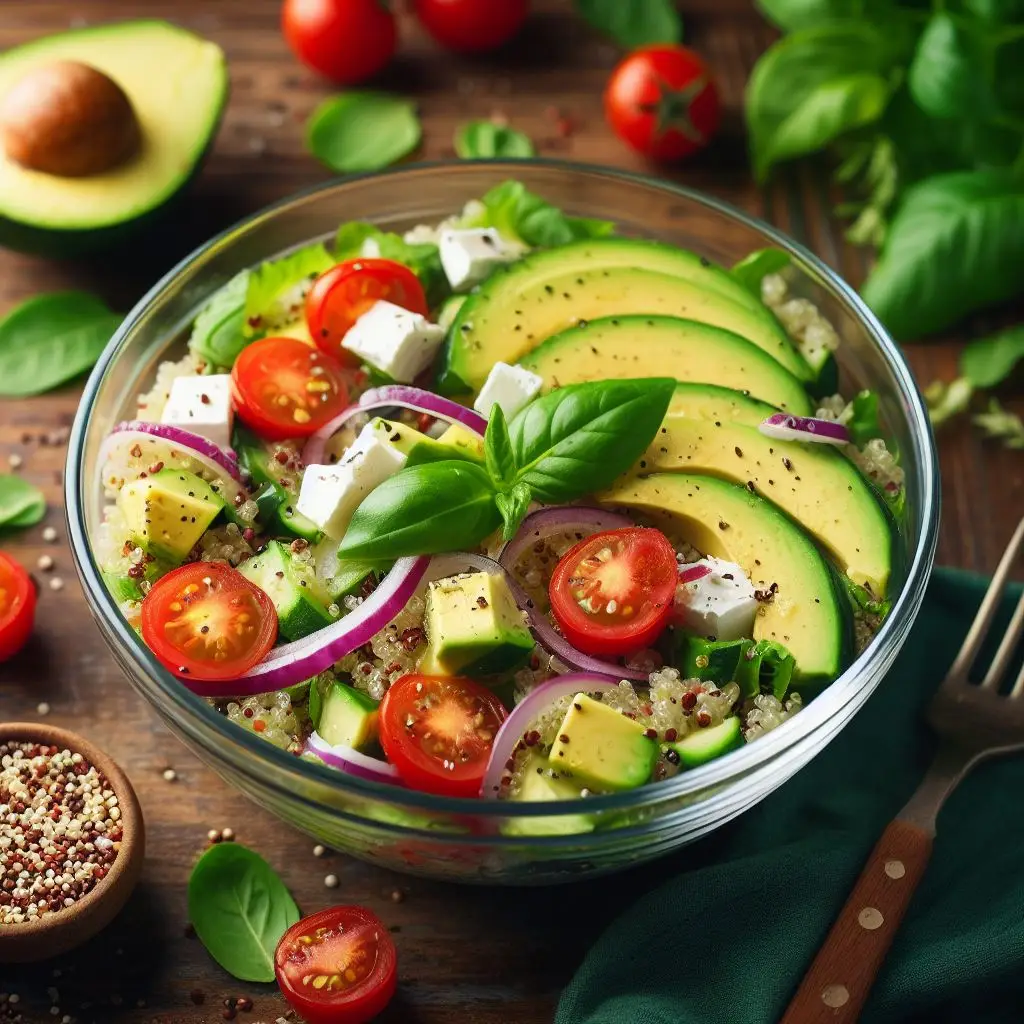

Prepare a quinoa salad with colorful vegetables and a light vinaigrette. Quinoa is an excellent source of protein and complex carbs, making it a great pre-workout option.
13. Cucumber and Cottage Cheese
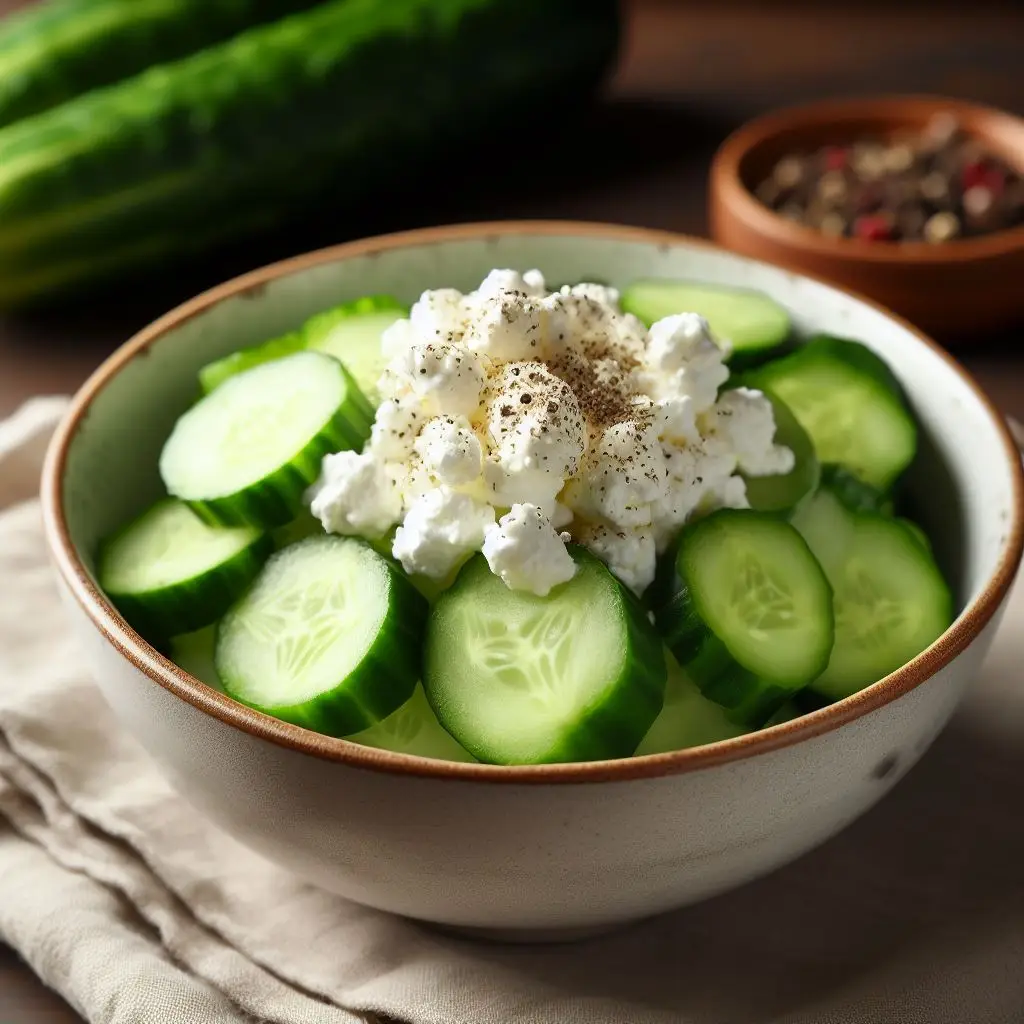

Crisp cucumber slices with cottage cheese are a hydrating and protein-rich choice for those looking for a low-calorie pre-workout snack.
14. Chia Pudding
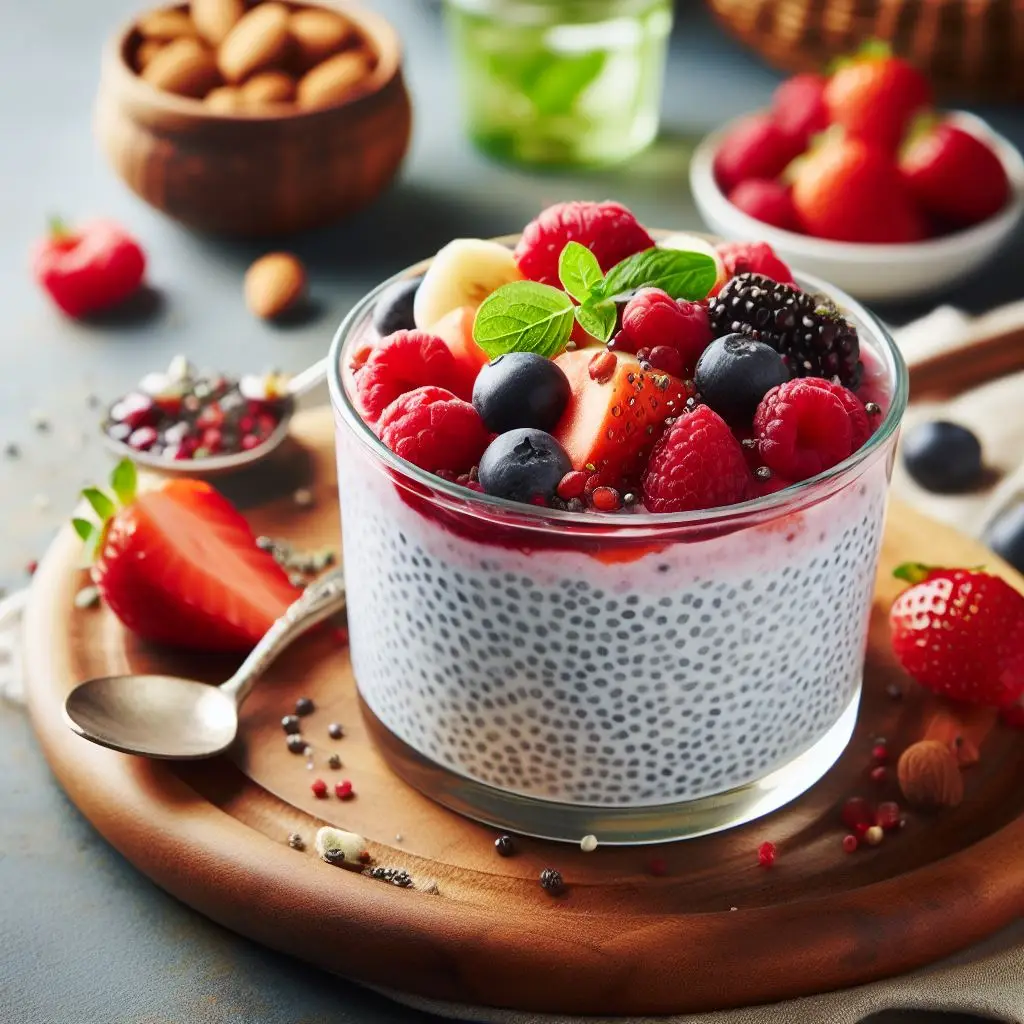

Make chia pudding with almond milk and top it with fresh fruit. Chia seeds are a great source of omega-3 fatty acids, fiber, and protein.
15. Sliced Turkey and Avocado
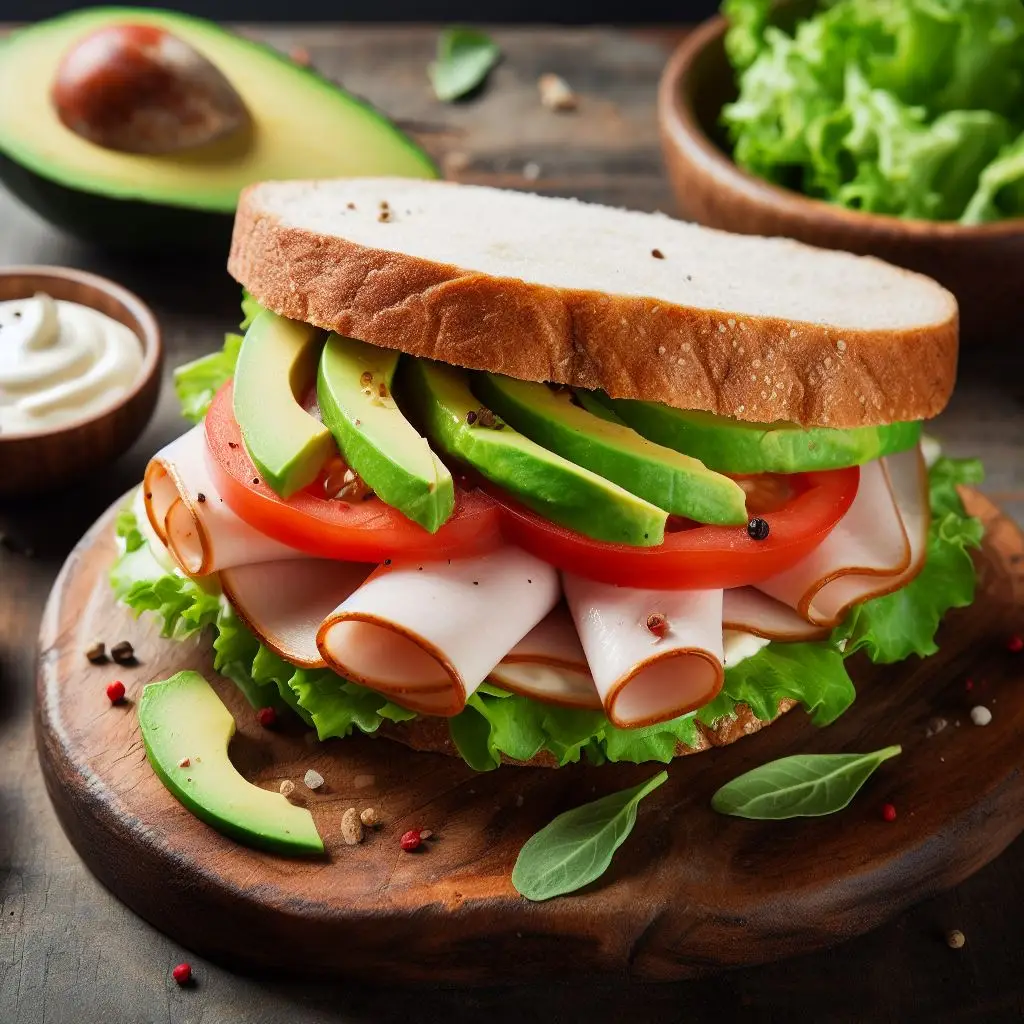

Wrap slices of turkey around avocado wedges for a protein-rich and satisfying pre-workout snack.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Pre-Workout Snack
Now that you know the benefits of pre-workout nutrition, you might be wondering how to choose the best snack for your needs. There are a few factors to consider when selecting a pre-workout snack, such as:
- Timing: Ideally, you should eat your pre-workout snack about 30 to 60 minutes before your exercise session. This will give your body enough time to digest the food and use it as fuel. However, this may vary depending on your individual preferences and metabolism. Experiment with different timings and see what works best for you.
- Macronutrients: Macronutrients are the three main components of food: carbohydrates, protein, and fat. Each of them plays a different role in pre-workout nutrition. Carbohydrates are the primary source of energy for your muscles and brain. Protein helps repair and build muscle tissue and prevent muscle breakdown. Fat provides long-lasting energy and supports hormone production and absorption of fat-soluble vitamins. A balanced pre-workout snack should contain a combination of these macronutrients, with an emphasis on carbohydrates and protein.
- Calories: The amount of calories you need for your pre-workout snack depends on your body weight, activity level, and fitness goals. Generally, you should aim for about 100 to 300 calories for your pre-workout snack. Too few calories may not provide enough energy, while too many calories may cause digestive discomfort or weight gain.
- Hydration: Hydration is another crucial aspect of pre-workout nutrition. Water helps transport nutrients and oxygen to your muscles, regulate your body temperature, and prevent dehydration. Dehydration can impair your performance, cause fatigue, headaches, and cramps. Therefore, you should drink plenty of water before, during, and after your workout. You can also add some electrolytes to your water to replenish the minerals lost through sweat.
WHAT SHOULD YOU EAT TO FUEL YOUR WORKOUT?
What you eat before a workout can have a significant impact on your performance and recovery. The best foods to eat are those that provide your body with the energy, strength, and nutrients it needs to perform at its best. The type and amount of food you eat depend on the individual, their goals, the type of workout, and how much time before their workout. The main macronutrients to consider are carbohydrates, protein, and fat.
Carbohydrates are your body’s preferred fuel source, especially for short and high intensity exercises. They are stored as glycogen in your muscles and liver, and are used to power your movements. Eating carbs before a workout can increase your glycogen stores and prevent them from running low during exercise. This can help you maintain your intensity and delay fatigue.
Carbs can also stimulate insulin, which helps transport glucose and amino acids into your muscles, enhancing their growth and repair, Protein is essential for muscle protein synthesis, which is the process of building and repairing muscle tissue. Eating protein before a workout can increase this process and reduce muscle breakdown. Protein can also provide some energy and help you feel full and satisfied. Some studies have shown that pre-workout protein intake can improve athletic performance, increase muscle mass, enhance muscle recovery, and boost strength and power.
Fat is the main fuel source for longer and moderate-to-low intensity exercises. It provides more calories per gram than carbs or protein, and can help sustain your energy levels for longer workouts. Fat can also help absorb fat-soluble vitamins and provide essential fatty acids for your health. However, fat takes longer to digest than carbs or protein, so you should avoid eating too much fat right before a workout, as it can cause stomach discomfort or slow down your digestion.
As a general guideline, you should consume a large meal with protein, complex carbohydrates, and healthy fats 3-4 hours before an activity, and top up glycogen stores 30-60 minutes before a workout with a small pre-workout snack of simple carbohydrates. However, the optimal amount and timing of pre-workout nutrition may vary depending on factors such as age, gender, body weight, fitness level, and intensity of exercise.
IS IT NECESSARY TO EAT BEFORE A WORKOUT?
Not everyone needs a pre-workout snack. If you are working out first thing in the morning or long after a meal you may need to consume a small pre-workout snack to ensure that you are adequately fueled, however, if you are working out shortly after consuming a full meal, in many cases, there is no need for an additional pre-workout snack.
Although athletes will have special and specific needs, if you are a general exerciser who is looking to support your overall health you likely don’t need targeted and strategic exercise nutrition strategies, you simply want to ensure that you consume some carbohydrates and a little protein to fuel your activity. However, some people may prefer to eat something before a workout to prevent hunger, low blood sugar, or gastrointestinal discomfort.
WHAT ARE SOME GOOD PRE-WORKOUT SNACKS FOR EARLY MORNING WORKOUTS?
If you are someone who workouts or goes to the gym first thing in the morning, there is no need to wake up 3 to 4 hours before your workout to consume a complete meal! What and how much to eat before a morning workout depends on your individual health, your goals, and the type of workout you are doing.
WHAT ARE THE BEST PRE-WORKOUT SNACKS FOR WEIGHT LOSS?
The best pre-workout snacks for weight loss are the same as the best pre-workout snacks for general health and optimal performance. To lose weight, you must create a calorie deficit. Meaning, you must expend more calories than you are consuming via food and beverage to ensure that your body is using stored energy (i.e. body fat). Therefore, to support a weight loss goal, you can consume any pre-workout snack as long as the calories from that snack fit within your daily calorie intake to create a calorie deficit. However, some studies suggest that eating a high-protein snack before exercise may increase fat oxidation and reduce appetite, which could be beneficial for weight loss.